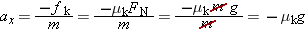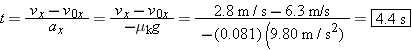| *115. |
 Refer to Multiple-Concept Example 10 for help in solving problems like this one. An ice skater is gliding horizontally across the ice with an initial velocity of Refer to Multiple-Concept Example 10 for help in solving problems like this one. An ice skater is gliding horizontally across the ice with an initial velocity of 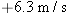 . The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ice and the skate blades is 0.081, and air resistance is negligible. How much time elapses before her velocity is reduced to . The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ice and the skate blades is 0.081, and air resistance is negligible. How much time elapses before her velocity is reduced to 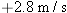 ? ?Answer:
4.4 s  REASONING Let us assume that the skater is moving horizontally along the REASONING Let us assume that the skater is moving horizontally along the 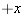 axis. The time axis. The time 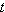 it takes for the skater to reduce her velocity to it takes for the skater to reduce her velocity to 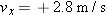 from from 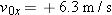 can be obtained from one of the equations of kinematics: can be obtained from one of the equations of kinematics:
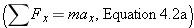 in the following manner. The kinetic frictional force is the only horizontal force that acts on the skater, and, since it is a resistive force, it acts opposite to the direction of the motion. Thus, the net force in the in the following manner. The kinetic frictional force is the only horizontal force that acts on the skater, and, since it is a resistive force, it acts opposite to the direction of the motion. Thus, the net force in the 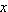 direction is direction is 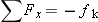 , where , where 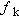 is the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force. is the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force.Therefore, the acceleration of the skater is
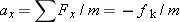 . .The magnitude of the frictional force is
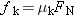 (Equation 4.8), where (Equation 4.8), where 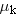 is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ice and the skate blades and is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ice and the skate blades and 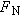 is the magnitude of the normal force. There are two vertical forces acting on the skater: the upward-acting normal force is the magnitude of the normal force. There are two vertical forces acting on the skater: the upward-acting normal force 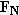 and the downward pull of gravity (her weight) and the downward pull of gravity (her weight) 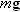 . Since the skater has no vertical acceleration, Newton's second law in the vertical direction gives (taking upward as the positive direction) . Since the skater has no vertical acceleration, Newton's second law in the vertical direction gives (taking upward as the positive direction) 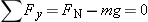 . Therefore, the magnitude of the normal force is . Therefore, the magnitude of the normal force is 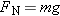 and the magnitude of the acceleration is and the magnitude of the acceleration is
SOLUTION Solving the equation
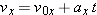 for the time and substituting the expression above for the acceleration yields for the time and substituting the expression above for the acceleration yields
|