Work-Energy Theorem: Compare W to ΔE
Topics and Files
Mechanics Topic
- Work-energy theorem, conservation of energy
Capstone File
- 32 Work and Energy.cap
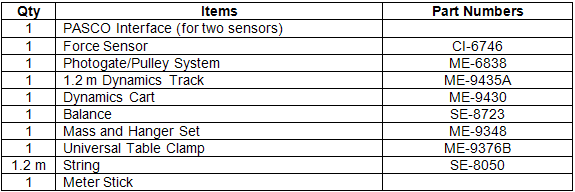
Equipment List
Introduction
The purpose of this lab is to compare the work done on an object to the change in kinetic energy of the object. Use the force sensor to measure the force applied to the cart. Use the photogate/pulley system to measure the motion of the cart as it is pulled by the weight of the hanging mass. Use Capstone to record and display the force, motion, work done, and the calculation of kinetic energy. Compare the work done to the change of kinetic energy.Background
For an object with mass m that experiences a net force Fnet over a distance d that is parallel to the net force, the equation below shows the work done.( 1 )
W = Fnetd
( 2 )
W = Δ KE = KEf − KEi =
mvf2 −
mvi2
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 1 |
| 2 |