Conservation of Energy
Topics and Files
Mechanics Topics
- GPE, KE, conservation of energy
- Transform energy, conservation of energy
Capstone Files
- 25 Discover Energy.cap
- 31 Pendulum Energy.cap
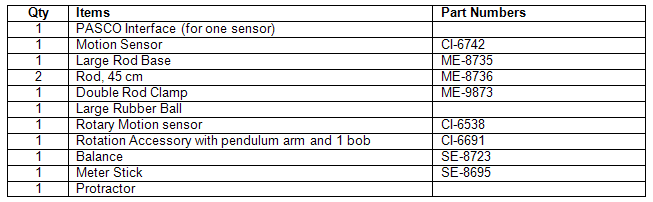
Equipment List
Introduction
This lab has two parts. The purpose of Experiment 1 is to investigate the relationship between kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy for a falling object. Use the motion sensor to measure the motion of a ball as it falls away from the sensor. Use Capstone to record and display the motion. Compare the calculated values of kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy. Also compare the sum of these two near the beginning of the fall to the sum near the end of the fall. The purpose of Experiment 2 is to investigate the transformations of energy that happen during the motion of a simple pendulum, and to study the conservation of mechanical energy. Use the rotary motion sensor to measure the motion of a simple physical pendulum. Use Capstone to record and display the motion and to display the calculations of period, kinetic energy, potential energy, and total energy of the pendulum. Compare the total energy at the beginning to the total energy at the end.Background
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Gravitational potential energy (GPE) is the energy of an object due to its vertical position relative to a reference point (such as the surface of the Earth). When an object is lifted a certain vertical distance, it gains gravitational potential energy. How much it has depends on its weight (mg) and the vertical distance. As the object falls, the gravitational potential decreases:( 1 )
GPE = mgh
( 2 )
KE =
mv2
| 1 |
| 2 |
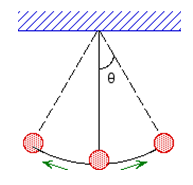
Figure 1
( 3 )
K =
mv2,U = mgh = mg(L − L cos θ)
| 1 |
| 2 |