Graphs of Parent Functions
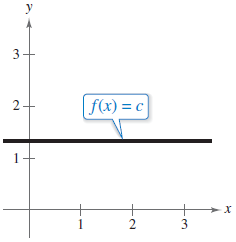
A horizontal line labeled f(x) = c is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The line enters the window in the second quadrant, goes horizontally right, crosses the y-axis at y = 1.25, continues horizontally right, and exits the window in the first quadrant.
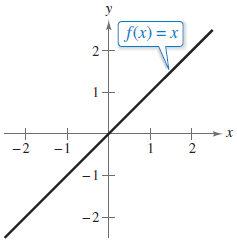
A line labeled f(x) = x is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The line enters the window in the third quadrant, goes up and right, passes through the point (−1, −1), crosses the x-axis at the origin, passes through the point (1, 1), and exits the window in the first quadrant.
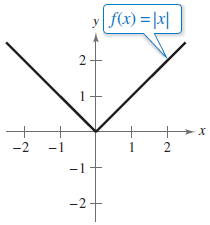
A function labeled f(x) = |x| is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The function enters the window in the second quadrant, goes down and right, passes through the point (−1, 1), changes direction at the origin, goes up and right, passes through the point (1, 1), and exits the window in the first quadrant.
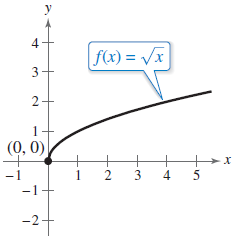
A curve labeled f(x) = √(x) is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The curve begins at the origin, goes up and right becoming less steep, passes through the point (1, 1), and exits the window in the first quadrant.
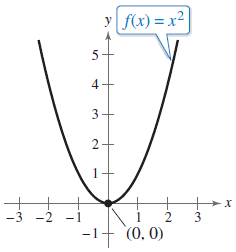
A curve labeled f(x) = x2 is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The curve enters the window in the second quadrant, goes down and right becoming less steep, passes through the point (−1, 1), changes direction at the origin, goes up and right becoming more steep, passes through the point (1, 1), and exits the window in the first quadrant.
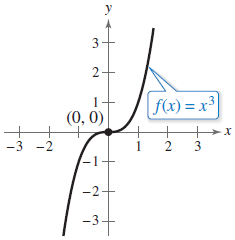
A curve labeled f(x) = x3 is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The curve enters the window in the third quadrant, goes up and right becoming less steep, passes through the point (−1, −1), becomes nearly horizontal as it crosses the origin, goes up and right becoming more steep, passes through the point (1, 1), and exits the window in the first quadrant.

A curve with 2 parts labeled f(x) = 1 ⁄ x is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. The first part of the curve enters the window nearly horizontal below the negative x-axis, goes down and right becoming more steep, passes through the point (−2, −0.5), passes through the point (−1, −1), and exits the window nearly vertical to the left of the negative y-axis. The second part of the curve enters the window nearly vertical to the right of the positive y-axis, goes down and right becoming less steep, passes through the point (1, 1), passes through the point (2, 0.5), and exits the window nearly horizontal above the positive x-axis.
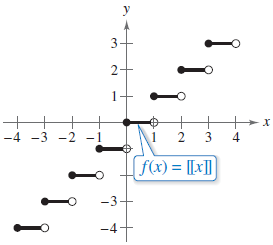
A function with 6 parts labeled f(x) = [[x]] is graphed on the x y-coordinate plane. All 6 parts are horizontal line segments that begin with a closed point and end with an open point. The starting and ending points of each part is as follows.
- The first part starts at (−3, −3) and ends at (−2, −3).
- The second part starts at (−2, −2) and ends at (−1, −2).
- The third part starts at (−1, −1) and ends at (0, −1).
- The fourth part starts at (0, 0) and ends at (1, 0).
- The fifth part starts at (1, 1) and ends at (2, 1).
- The sixth part starts at (2, 2) and ends at (3, 2).