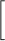
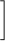Appendix C: Uncertainty Formulae
For a function F of multiple variables x, each with uncertaintyσx,
the square of the uncertainty in F is given as
( 1 )
σF2 = Σi
σxi
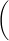 |
| δ F |
| δ xi |
 | 2 |
Addition rule: F(x1,x2) = x1 + x2
( 2 )
| σF2 | = |
| +
| ||||||||||||
| = | σx12 + σx22 | ||||||||||||||
( 3 )
L = x1 + x2
( 4 )
σL2 =
σx1
+
σx2
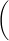 |
| δF |
| δx1 |
 | 2 |
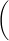 |
| δF |
| δx2 |
 | 2 |
x1
= (1.23 ± 0.02) m and x2
= (4.17 ± 0.01) m, then
( 5 )
| σL2 | = | ((0.02)2 + (0.01)2) m2 |
| = | (4 × 10−4 + 1 × 10−4) m2 | |
| = | 5 × 10−4 m2 | |
| σL | = | 2.2 × 10−2 m, and |
| L | = | (5.40 ± 0.02) m |
Product rule: F(A,B,C) = kAmBnCp
( 6 )
| σF2 | = |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| = |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| = | F2
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| σF | = | F
|
F = k
| Q1Q2 |
| r2 |
( 7 )
σF = F
 |
|
Q1 = (6.1 ± 0.4)
µC, Q2 = (4.7 ± 0.3)
µC, r = (0.025 ± 0.003)
m.
F = 8.99 × 109
= 4.1 × 102 N
| (6.1 × 10−6)(4.7 × 10−6) |
| 0.0252 |
( 8 )
| σF | = | 4.1 × 102
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| = | 4.1 × 102
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| = | (4.1 × 102) (0.26) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| = | 1.07 × 102 N |
F = (410 ± 100) N