3.4 Electromagnetic Spectrum
Pre-Lecture Reading 3.4
-
•Astronomy Today, 8th Edition (Chaisson & McMillan)
-
•Astronomy Today, 7th Edition (Chaisson & McMillan)
-
•Astronomy Today, 6th Edition (Chaisson & McMillan)
Video Lecture
-
•Electromagnetic Spectrum (5:14)
Supplementary Notes
Types of Light
-
•See Types of Light.
-
•Visible light—the light that we can see with our eyes—is only a tiny sliver of the entire electromagnetic spectrum, with wavelengths between ≈700 nm (red) and ≈400 nm (violet).
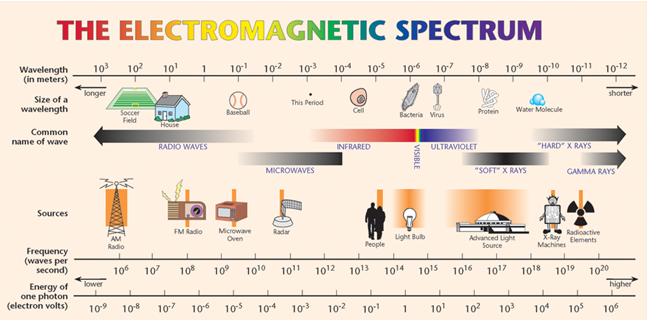
Figure 1: Image Credit: Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Light Wave Properties
Waves in general
-
•See Particle vs. Wave Motion.
Light waves
Example:
If you double a light wave's frequency, you double its energy.
If you double a light wave's frequency, you double its energy.
-
•Solving for λ and ν yields:
Example:
Consider a 1-m radio wave. Hence,
Consider a 1-m radio wave. Hence,
λ = 1 m
and ν =
= 3 × 108 s−1 = 3 × 108 Hz.
| (3 × 108 m/s) |
| (1 m) |
Example:
Consider a 108-Hz radio wave. Hence,
Consider a 108-Hz radio wave. Hence,
ν = 108 Hz
and λ =
= 3 m.
| (3 × 108 m/s) |
| (108 Hz) |
For λ measured in nm, µm, mm, cm, m, and km, the following values of c, respectively, can be used to simplify calculations:
-
•c = 3.00 × 1017 nm/s
-
•c = 3.00 × 1014 µm/s
-
•c = 3.00 × 1011 mm/s
-
•c = 3.00 × 1010 cm/s
-
•c = 3.00 × 108 m/s
-
•c = 3.00 × 105 km/s
Assignment 2
-
•Do Question 2.
